Cartogram Map
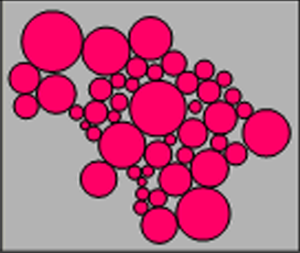 Cartogram maps display
variables by varying area size. MapViewer's
can create Dorling, contiguous, and noncontiguous cartograms. In a Dorling
cartogram the areas are replaced by circles and the circles are scaled
according to a variable. The maps can be controlled so the circles do
not overlap and are positioned as close to the base map's centroids as
possible. In a noncontiguous cartogram, polygon shapes are disconnected,
and the area is proportional to the selected variable. In a contiguous
cartogram, polygons remain connected, and their size and shape are distorted
as the area is scaled to the selected variable.
Cartogram maps display
variables by varying area size. MapViewer's
can create Dorling, contiguous, and noncontiguous cartograms. In a Dorling
cartogram the areas are replaced by circles and the circles are scaled
according to a variable. The maps can be controlled so the circles do
not overlap and are positioned as close to the base map's centroids as
possible. In a noncontiguous cartogram, polygon shapes are disconnected,
and the area is proportional to the selected variable. In a contiguous
cartogram, polygons remain connected, and their size and shape are distorted
as the area is scaled to the selected variable.
Creating and Editing a Cartogram Map
Click the Map | Create Map |
Cartogram command  to
create a cartogram map. Edit cartogram map properties in the Property
Manager.
to
create a cartogram map. Edit cartogram map properties in the Property
Manager.
See Creating
and Editing Thematic Maps for information on creating a map, changing
a map to another map type, and changing map properties.
Cartogram Map Properties
The cartogram map Property
Manager has General, Data
Labels, Info, and
Map pages. Click the preceding
hyperlinks for information on properties in each of the property manager
pages.
Map Page
Select cartogram type and edit cartogram specific properties in the
Map page of the Property
Manager.
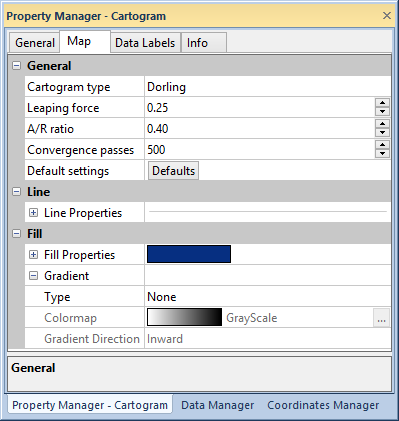
Edit cartogram map properties in the Map
page of the Property Manager.
General
The General section properties
select the cartogram type and edit the cartogram map. Click the Cartogram type list to select a
Dorling, Non-contiguous, or Contiguous cartogram.
Generating a contiguous cartogram map can take a few seconds, depending
on the cartogram map settings, data set, and your computer's capabilities.
Unlike other gridding operations, contiguous
cartogram map creation cannot be cancelled.
The Leaping force controls
the distance the circles or polygons move in each convergence pass. The
circles or polygons move away from the previous position with each pass.
Type a value between 0.01 and 1.00 in the Leaping
force field or click the  buttons to set the Leaping force.
A Leaping force of 1.0
moves the circle far away from the previous position with each pass. A
Leaping force of 0.01moves the
circles very little with each pass. Dorling
and Non-contiguous
cartograms have the Leaping force
property.
buttons to set the Leaping force.
A Leaping force of 1.0
moves the circle far away from the previous position with each pass. A
Leaping force of 0.01moves the
circles very little with each pass. Dorling
and Non-contiguous
cartograms have the Leaping force
property.
The A/R ratio is the attraction/repulsion
ratio that controls circle or polygon overlap. Type a value between 0.01
and 1.00 in the A/R ratio field
or click the  buttons
to set the A/R ratio. An A/R ratio of 1.0 makes the circles
overlap each other. An A/R Ratio
of 0.01 leads to minimum overlap. Dorling
and Non-contiguous cartograms
have the A/R ratio
property.
buttons
to set the A/R ratio. An A/R ratio of 1.0 makes the circles
overlap each other. An A/R Ratio
of 0.01 leads to minimum overlap. Dorling
and Non-contiguous cartograms
have the A/R ratio
property.
Convergence passes controls
the number of times the circles are repositioned with the Leaping
force and A/R ratio values.
Only Dorling cartograms have
the Convergence passes property.
Click the Defaluts button in
the Default settings field to
return the cartogram to the MapViewer
defaults. Only Dorling and Non-contiguous cartograms have
the Defalut settings option.
Line
Set the line properties for the cartogram map in the Line
section. See the line properties
help page for more information on editing cartogram line properties.
Fill
Set the cartogram fill properties in the Fill
section. See the fill
properties help page for more information on editing cartogram map
fill properties. Apply a gradient fill to the cartogram map by selecting
Linear or Radial
from the Type list. Click on
the Colormap selection to pick
a predefined colormap for the gradient, or click the  button to create a custom colormap in the Colormap
dialog. Select a Vertical, Horizontal, Inward,
or Outward gradient direction
in the Gradient Direction list.
button to create a custom colormap in the Colormap
dialog. Select a Vertical, Horizontal, Inward,
or Outward gradient direction
in the Gradient Direction list.
See Also
Property Manager
 Cartogram maps display
variables by varying area size. MapViewer's
can create Dorling, contiguous, and noncontiguous cartograms. In a Dorling
cartogram the areas are replaced by circles and the circles are scaled
according to a variable. The maps can be controlled so the circles do
not overlap and are positioned as close to the base map's centroids as
possible. In a noncontiguous cartogram, polygon shapes are disconnected,
and the area is proportional to the selected variable. In a contiguous
cartogram, polygons remain connected, and their size and shape are distorted
as the area is scaled to the selected variable.
Cartogram maps display
variables by varying area size. MapViewer's
can create Dorling, contiguous, and noncontiguous cartograms. In a Dorling
cartogram the areas are replaced by circles and the circles are scaled
according to a variable. The maps can be controlled so the circles do
not overlap and are positioned as close to the base map's centroids as
possible. In a noncontiguous cartogram, polygon shapes are disconnected,
and the area is proportional to the selected variable. In a contiguous
cartogram, polygons remain connected, and their size and shape are distorted
as the area is scaled to the selected variable. to
create a cartogram map. Edit cartogram map properties in the
to
create a cartogram map. Edit cartogram map properties in the 
 buttons to set the
buttons to set the  button to create a custom colormap in the
button to create a custom colormap in the