 button to display the Natural
Neighbor Options dialog. For more information about anisotropy
options see Anisotropy.
button to display the Natural
Neighbor Options dialog. For more information about anisotropy
options see Anisotropy.The Natural Neighbor gridding method is quite popular in some fields. What is Natural Neighbor interpolation? Consider a set of Thiessen polygons (the dual of a Delaunay triangulation). If a new point (target) were added to the data set, these Thiessen polygons would be modified. In fact, some of the polygons would shrink in size, while none would increase in size. The area associated with the target's Thiessen polygon that was taken from an existing polygon is called the "borrowed area." The Natural Neighbor interpolation algorithm uses a weighted average of the neighboring observations, where the weights are proportional to the "borrowed area."
The Natural Neighbor method does not extrapolate data beyond the convex hull of the data locations (i.e. the outline of the Thiessen polygons).
In the Property
Manager Gridding page, select Natural
Neighbor as the
Gridding
method and then click
the Advanced Options
 button to display the Natural
Neighbor Options dialog. For more information about anisotropy
options see Anisotropy.
button to display the Natural
Neighbor Options dialog. For more information about anisotropy
options see Anisotropy.
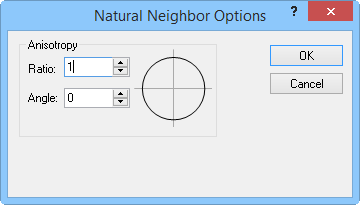
Set Anisotropy options in the Natural Neighbor Options dialog.
See Also